Continuous monitoring and optimization of expenses are necessary to maintain and improve profitability. Location is a critical factor, as it influences foot traffic, competition, and rent costs, all of which affect the break-even point. Stores may experience increased sales during holidays or specific seasons, temporarily lowering the break-even point.
How to Calculate the Break-Even Point
That’s why they constantly try to change elements in the formulas reduce the number of units need to produce and increase profitability. Break-even analysis, or the comparison of sales to fixed costs, is a tool used by businesses and stock and option traders. It is essential in determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
By using the formula to calculate your break-even revenue, you can make informed decisions about pricing, cost-cutting measures, and sales targets. Whether you are a small startup or an established business, calculating your break-even point helps ensure your business stays profitable and financially sound. Production managers and executives have to be keenly aware of their level of sales and how close they are to covering fixed and variable costs at all times.
- From there, you can decide on pricing, production, and sales targets so your business can stay on the right track from the get-go.
- By looking at each component individually, you can start to ask yourself critical questions about your pricing and costs.
- The breakeven point is the production level at which total revenues for a product equal total expenses.
- Knowing a company’s fixed costs and contribution margin will allow them to determine their break-even point.
Break-Even Point in Units
After reaching the break-even point, a grocery store typically achieves a net profit margin of between 1% and 3%. Competitive pricing may increase sales but could require higher volumes to cover costs. Seasonal fluctuations can significantly impact a grocery store’s sales, affecting the time it takes to reach the break-even point.
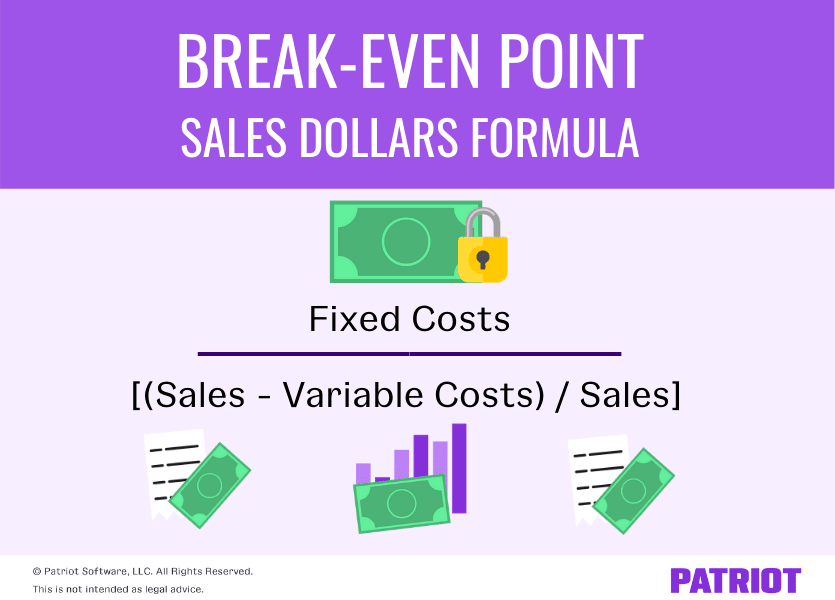

In other words, the breakeven point is equal to the total fixed costs divided by the difference between the unit price and variable costs. Note that in this formula, fixed costs are stated as a total of all overhead for the firm, whereas 4 factors influencing local government financial decisions price and variable costs are stated as per unit costs—the price for each product unit sold. It is also possible to calculate how many units need to be sold to cover the fixed costs, which will result in the company breaking even.
And as much as we think a lower price means more buyers, studies actually show that consumers rely on price to determine the quality of a product or service. Ideally, you should conduct this financial analysis before you start a business so you have a good idea of the risk involved. In other words, you should figure out if the business is worth it.
Variable costs are calculated on a per-unit basis, so if you produce or sell more units, the variable cost will increase. Some common examples of variable costs are commissions on sales, delivery charges, and temporary labor wages. When starting a new business, this analysis can help you find out if your business idea is financially viable before you invest too much time or money. From there, you can decide on pricing, production, and sales targets so your business can stay on the right track from the get-go.
Note that a product’s contribution margin may change (i.e. it may become more or less efficient to manufacture additional goods). Alternatively, option two is producing more units without lowering production costs. Or, a potential third option, which is to examine how to reduce fixed costs.
However, it might be too complicated to do the calculation, so you can spare yourself some time and effort by using this Break-even Calculator. All you need to do is provide information about your fixed costs, and your cost and revenue per unit. To make the analysis even more precise, you can input how many units you expect to sell per month. Next, you need to look at fixed costs to determine the break-even quantity. For this new product, you estimate that the fixed costs for the year will be $10,000. Using the break-even formula, we can calculate that the business must sell 1,250 units in a year to break even.
It aids in strategic decision-making regarding pricing, cost control, and sales targets. If the stock is trading at a market price of $170, for example, the trader has a profit of $6 (breakeven of $176 minus the current market price of $170). Assume an investor pays a $4 premium for a Meta (formerly Facebook) put option with a $180 strike price. That allows the put buyer to sell 100 shares of Meta stock (META) at $180 per share until the option’s expiration date. The put position’s breakeven price is $180 minus the $4 premium, or $176. If the stock is trading above that price, then the benefit of the option has not exceeded its cost.
Knowing this metric helps you create targets that will prevent a business from losing money. If your price is too high, you might be falling short of your break-even point because customers won’t buy at that price. Lowering your selling price will increase the sales needed to break even. But this can be offset by the increased volume of purchases from new customers.